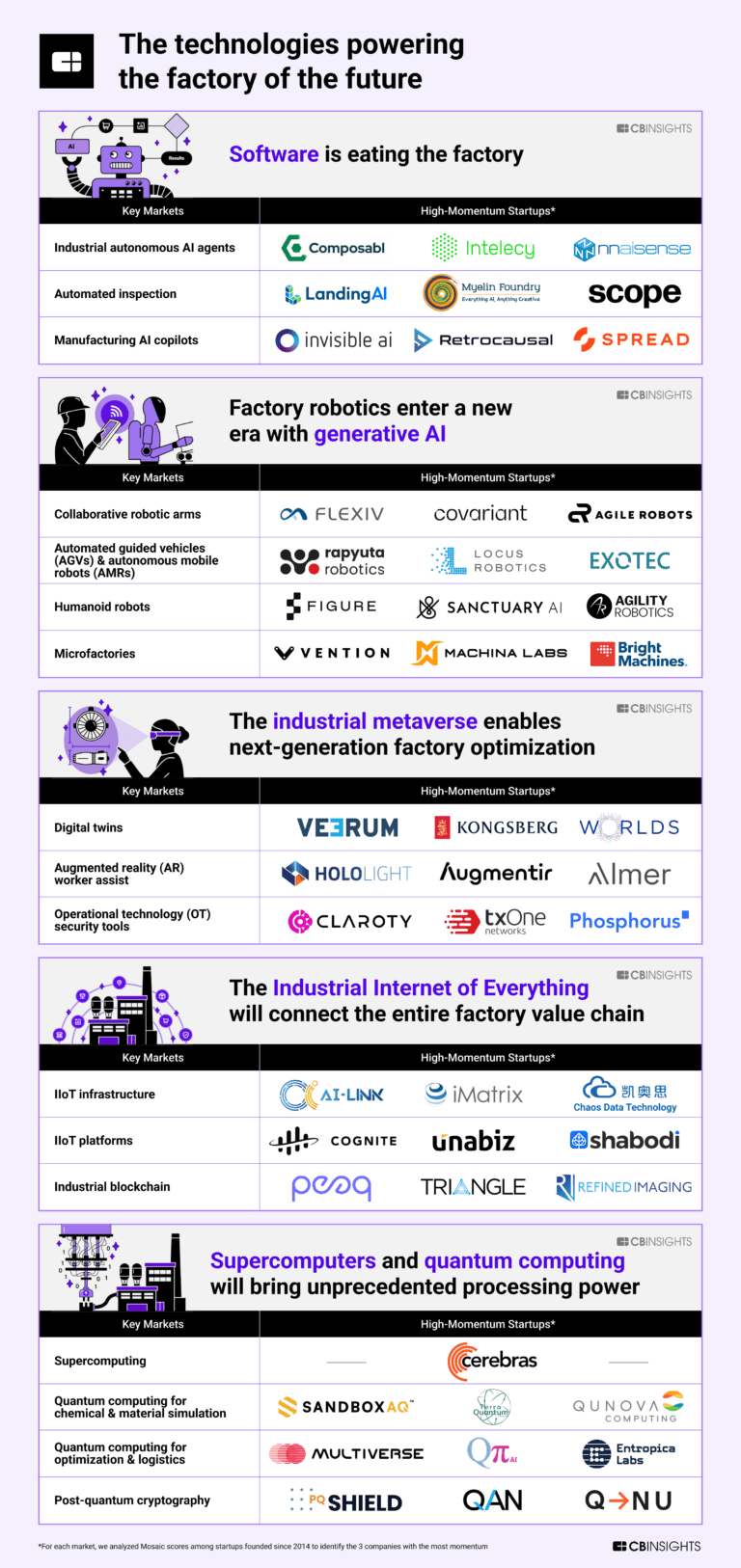
Multiverse Computing
Founded Year
2019Stage
Series B | AliveTotal Raised
$339.91MLast Raised
$215M | 5 mos agoRevenue
$0000Mosaic Score The Mosaic Score is an algorithm that measures the overall financial health and market potential of private companies.
-6 points in the past 30 days
About Multiverse Computing
Multiverse Computing works in quantum artificial intelligence (AI) and focuses on optimization within various sectors. The company provides AI model compression technology aimed at improving the performance of AI systems. Multiverse Computing serves sectors such as finance, energy, manufacturing, health and life sciences, engineering, aerospace, cybersecurity, defense, and chemistry. It was founded in 2019 and is based in San Sebastian, Spain.
Loading...
Multiverse Computing's Product Videos


Loading...
Research containing Multiverse Computing
Get data-driven expert analysis from the CB Insights Intelligence Unit.
CB Insights Intelligence Analysts have mentioned Multiverse Computing in 7 CB Insights research briefs, most recently on Oct 20, 2025.

Oct 20, 2025 report
Book of Scouting Reports: 2025’s Digital Health 50
Jul 10, 2025 report
State of Venture Q2’25 Report
May 16, 2025 report
Book of Scouting Reports: 2025’s AI 100
Apr 24, 2025 report
AI 100: The most promising artificial intelligence startups of 2025Expert Collections containing Multiverse Computing
Expert Collections are analyst-curated lists that highlight the companies you need to know in the most important technology spaces.
Multiverse Computing is included in 8 Expert Collections, including Quantum Tech.
Quantum Tech
628 items
This Expert Collection contains private and recently exited companies working on quantum computing, quantum communication, post-quantum cryptography, quantum sensors, and other quantum tech.
Grid and Utility
2,383 items
Companies that are developing and implementing new technologies to optimize the grid and utility sector. This includes, but is not limited to, distributed energy resources, infrastructure security, utility asset management, grid inspection, energy efficiency, grid storage, etc.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
14,182 items
Companies developing artificial intelligence solutions, including cross-industry applications, industry-specific products, and AI infrastructure solutions.
Semiconductors, Chips, and Advanced Electronics
7,494 items
Companies in the semiconductors & HPC space, including integrated device manufacturers (IDMs), fabless firms, semiconductor production equipment manufacturers, electronic design automation (EDA), advanced semiconductor material companies, and more
AI 100 (All Winners 2018-2025)
200 items
Generative AI
2,951 items
Companies working on generative AI applications and infrastructure.
Multiverse Computing Patents
Multiverse Computing has filed 40 patents.
The 3 most popular patent topics include:
- quantum information science
- machine learning
- quantum mechanics

Application Date | Grant Date | Title | Related Topics | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
9/1/2021 | 3/19/2024 | Quantum information science, Classification algorithms, Mathematical optimization, Units of information, Machine learning | Grant |
Application Date | 9/1/2021 |
|---|---|
Grant Date | 3/19/2024 |
Title | |
Related Topics | Quantum information science, Classification algorithms, Mathematical optimization, Units of information, Machine learning |
Status | Grant |
Latest Multiverse Computing News
Nov 13, 2025
Japanese Investors Pour $38 Billion Into European Tech Startups Dana LeighNovember 13, 2025 As Europe continues to evolve into one of the world’s most exciting startup hubs , capital is flowing in from all corners of the world. One of the most surprising? Japan. Whilst the UK and Europe have traditionally looked to raise funds from economies like the US, Japanese investors are slowly driving forward Europe’s deeptech sector. From AI to robotics and quantum computing, Japanese investors are piling in to get a piece of the action. But why? According to new research from NordicNinja VC and Dealroom, as reported by CNBC, Japanese investors have taken part in funding rounds worth more than €33 billion ($38 billion) since 2019. This increase is over 5 times more than before the 2019 trade deal between the EU and Japan came into play. The EU-Japan Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA) was designed to create one of the world’s largest free trade zones by reducing tariffs, making exports easier and facilitating movement of business people. At the time, Japan hadn’t invested much in European startups, but since then, a wave of corporates, including Mitsubishi, Sanden, Yamato Holdings and Marunouchi Innovation Partners, have started backing European startups directly according to CNBC. Japanese-linked VC firms like NordicNinja, Byfounders, and Toyota ’s Woven Capital have also come in for a piece of the action. And, according to Tomosaku Sohara, co-founder and managing partner at NordicNinja, SoftBank’s acquisition of Finnish gaming company Supercell was a turning point when it came to Japan playing a bigger role in Europe’s tech ecosystem. Japan’s interest in Europe comes at a time when it is grappling with its own economic growth. With an aging population and projected growth of less than 1% this year, it’s no surprise that investors are looking outwards. It’s also driven by geopolitical reasons. With political uncertainty between the US and China, Japan is looking to build its own alliances and potentially act at the main bridge to major Asian markets. One of the main sectors catching Japanese investors’ eyes is Europe’s deeptech scene. According to CNBC, in 2024, 70% of Japanese-linked deals in Europe were in deep tech and artificial intelligence, driving further interest in sectors like AI, energy and defence tech. Some of the top-funded companies with Japanese investment included: Wayve, the UK’s autonomous driving startup, which raised $1.05 billion in May 2024. Quantinuum, the Cambridge-based quantum computing firm, which secured €273 million in January 2024. Multiverse Computing, a Spanish company that applies quantum algorithms to finance and energy, which raised €189 million in June 2025. These rounds were backed by big Japanese named like Softbank, Mitsui and Toshiba. But one of the reasons that deeptech attracts so much capital is that it actually needs it. Deeptech startups need both capital and technical expertise to scale, this can be hard to find in Europe, but feels a natural match with Japan’s industrial giants. But with such big cultural differences between the two regions, securing investment isn’t always easy. Language barriers are one part of the equation, with only 20% – 30% of Japanese adults having some understanding of English. This can make negotiations difficult, especially when it comes to complicated investments. Japanese investors are also, in general, slightly more risk averse. As Europe has had longer to build trust in its startup ecosystem, investors are generally more at ease with taking risks. Japanese investors however, who have become more used to the predictable nature of big corporates, tend to be more methodical. This can mean slower fundraises and more time spent face-to-face, which can be very time intensive for founders. Japanese investment in Europe is expected to reach around €3 billion in 2025 according to Ninja and Dealroom’s report, although interest is definitely growing. With governments on both sides working on easier collaboration, founders across Europe could soon see even more capital coming in from Japanese funds. For Europe, it’s a great sign of confidence in its startup ecosystem and a way to diversify away from the US. For Japan, these investments could help them capitalise on European growth, especially as their economy struggles to grow. And who knows? Maybe the next generation of European deeptech startups will be built with Japanese capital. We will wait and see. Related Articles
Multiverse Computing Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When was Multiverse Computing founded?
Multiverse Computing was founded in 2019.
Where is Multiverse Computing's headquarters?
Multiverse Computing's headquarters is located at Paseo de Miramon 170, San Sebastian.
What is Multiverse Computing's latest funding round?
Multiverse Computing's latest funding round is Series B.
How much did Multiverse Computing raise?
Multiverse Computing raised a total of $339.91M.
Who are the investors of Multiverse Computing?
Investors of Multiverse Computing include Quantonation, CDP Venture Capital, EIC STEP Scale Up, SPRI Group, Sociedad Espanola para la Transformacion Tecnologica and 31 more.
Who are Multiverse Computing's competitors?
Competitors of Multiverse Computing include Classiq, Mistral AI, Cohere, QpiAI, Zapata Quantum and 7 more.
Loading...
Compare Multiverse Computing to Competitors

Classiq focuses on quantum computing software in the technology industry. The company offers a platform that enables the design, analysis, and execution of quantum circuits, transforming high-level functional models into optimized quantum circuits. The company primarily serves sectors such as optimization, machine learning, finance, and chemistry. It was founded in 2020 and is based in Tel Aviv, Israel.
Qedma develops software for the quantum computing industry. The company provides options for quantum error suppression and mitigation, along with characterization software for multi-qubit systems, which aim to support quantum computations. Its products are intended to work with existing quantum hardware across various platforms, targeting quantum hardware developers. It was founded in 2020 and is based in Tel Aviv, Israel.

SandboxAQ specializes in AI and advanced computing, focusing on large quantitative models across various sectors. Its primary offerings include AI simulation for drug discovery, materials science, cybersecurity, navigation, and medical diagnostics, all grounded in the laws of physics, chemistry, biology, and economics. SandboxAQ primarily serves sectors such as life sciences, financial services, and navigation, which require advanced computational models. It was founded in 2021 and is based in Palo Alto, California.
1QBit Information Technologies specializes in developing hardware-agnostic platforms for quantum and classical processors. It focuses on the intersection of quantum computing and artificial intelligence. The company offers services that include optimization, simulation, and machine learning solutions designed to improve alongside advancements in computational hardware. It was founded in 2012 and is based in Vancouver, Canada.

Kvantify specializes in advanced quantum computing solutions for various business sectors. The company offers off-the-shelf and custom software designed to tackle complex computational challenges, with a focus on being quantum-ready and leveraging cloud technology. Kvantify's primary customers include the life sciences, financial services, and logistics industries. It was founded in 2022 and is based in Kobenhavn, Denmark.

IQM specializes in superconducting quantum computers and operates within the quantum computing industry. The company offers a range of quantum computing products, including small-scale, advanced superconducting quantum computers with varying qubit counts, and a quantum cloud platform for research and development purposes. IQM primarily serves research laboratories, supercomputing centers, and industrial customers seeking to leverage quantum advantage. It was founded in 2018 and is based in Espoo, Finland.
Loading...