
Sierra
Founded Year
2023Stage
Series D | AliveTotal Raised
$635MValuation
$0000Last Raised
$350M | 2 mos agoRevenue
$0000Mosaic Score The Mosaic Score is an algorithm that measures the overall financial health and market potential of private companies.
+80 points in the past 30 days
About Sierra
Sierra provides a conversational artificial intelligence platform for businesses to deploy artificial intelligence agents for customer support across multiple channels and languages. Sierra's solutions can integrate with existing technology stacks and focus on security and compliance. It was founded in 2023 and is based in San Francisco, California.
Loading...
ESPs containing Sierra
The ESP matrix leverages data and analyst insight to identify and rank leading companies in a given technology landscape.
The customer service AI agents & copilots market comprises tools that automate client support inquiries and processes across multiple communication channels. These solutions converse with customers, answer questions, support inquiries, and resolve issues. Many can handle complex inquiries and complete processes end-to-end with minimal human oversight. They may also provide real-time assistance to …
Sierra named as Leader among 15 other companies, including NICE, Zendesk, and ServiceNow.
Loading...
Research containing Sierra
Get data-driven expert analysis from the CB Insights Intelligence Unit.
CB Insights Intelligence Analysts have mentioned Sierra in 13 CB Insights research briefs, most recently on Oct 30, 2025.
Oct 30, 2025 report
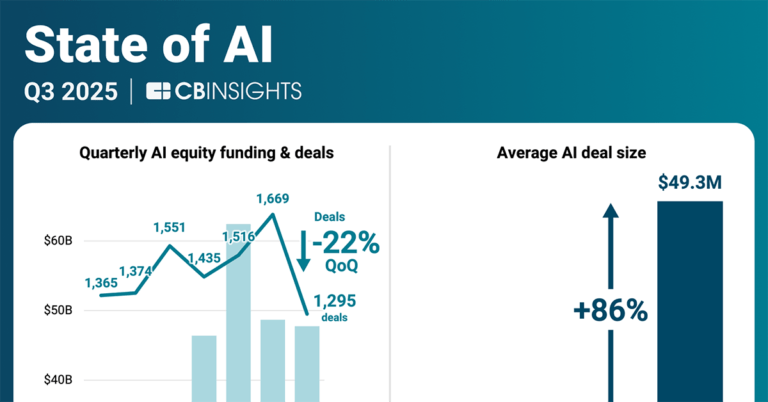
State of AI Q3’25 Report
Oct 20, 2025 report
Book of Scouting Reports: 2025’s Digital Health 50

Aug 14, 2025 report
Book of Scouting Reports: Enterprise AI Agents
Aug 4, 2025
3 markets fueling the shift to agentic commerce
May 16, 2025 report
Book of Scouting Reports: 2025’s AI 100
Apr 24, 2025 report
AI 100: The most promising artificial intelligence startups of 2025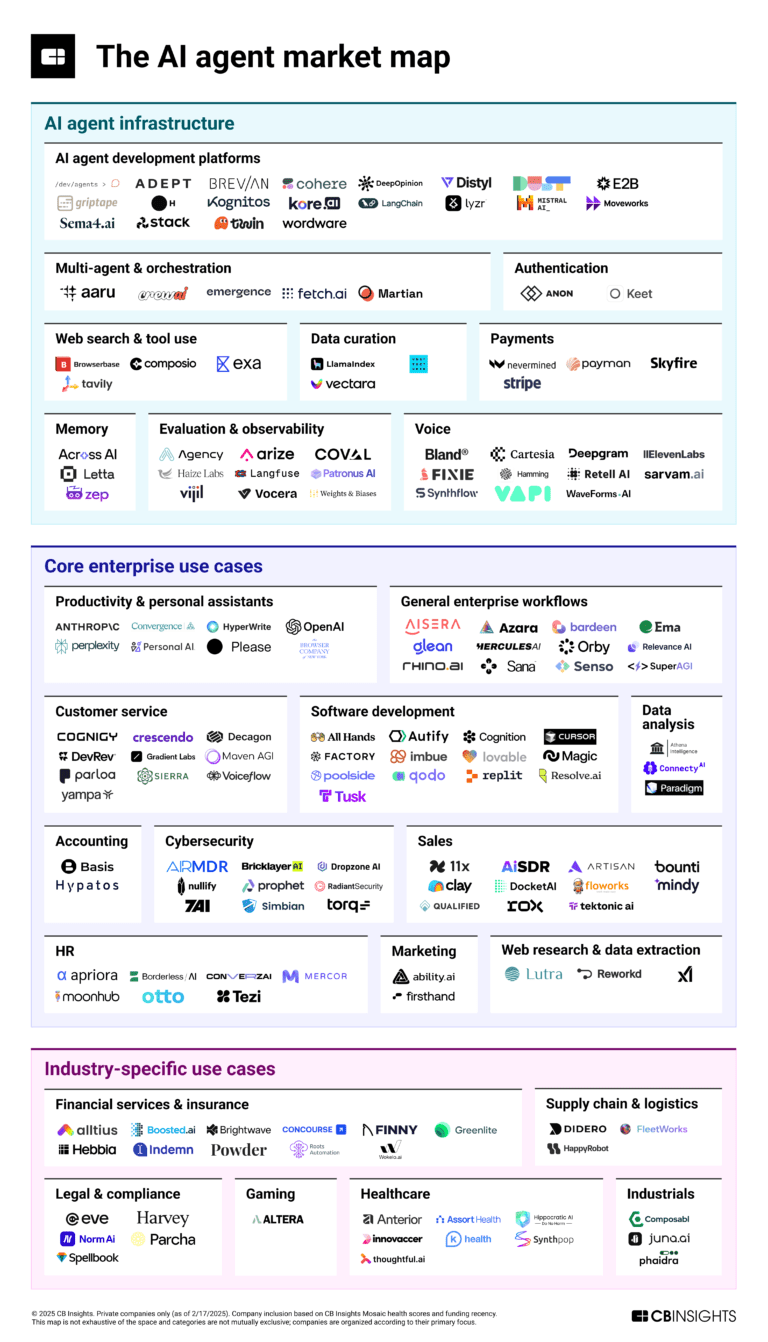
Mar 6, 2025
The AI agent market mapExpert Collections containing Sierra
Expert Collections are analyst-curated lists that highlight the companies you need to know in the most important technology spaces.
Sierra is included in 8 Expert Collections, including AI 100 (2024).
AI 100 (2024)
100 items
Generative AI
2,951 items
Companies working on generative AI applications and infrastructure.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
37,256 items
Companies developing artificial intelligence solutions, including cross-industry applications, industry-specific products, and AI infrastructure solutions.
Unicorns- Billion Dollar Startups
1,297 items
AI Agents & Copilots Market Map (August 2024)
322 items
Corresponds to the Enterprise AI Agents & Copilots Market Map: https://app.cbinsights.com/research/enterprise-ai-agents-copilots-market-map/
AI agents
376 items
Companies developing AI agent applications and agent-specific infrastructure. Includes pure-play emerging agent startups as well as companies building agent offerings with varying levels of autonomy. Not exhaustive.
Latest Sierra News
Nov 6, 2025
November 6, 2025, 6:16 pm IST Brett Taylor, co-founder and CEO of agentic AI startup Sierra and Chairman of OpenAI’s Board of Directors, recently articulated a transformative vision for artificial intelligence on CNBC’s Squawk Box. Speaking with Andrew Ross Sorkin, Taylor unveiled Sierra’s new Agent Data Platform, framing it within a broader discussion about the economic implications and future trajectory of AI, particularly its role in customer interaction and business operations. His central thesis was stark: “Every company’s AI agent is going to be more important than their website in a handful of years.” Taylor positioned Sierra at the vanguard of this shift, moving beyond mere chatbots to create truly agentic AI. This new generation of AI, powered by Sierra’s platform, is designed to possess memory, allowing it to “personalize their conversations not just over days, but over months and years.” This capability transcends the transactional nature of traditional customer service, enabling AI agents to act as sophisticated “concierges for your brand,” adept at handling both service inquiries and sales opportunities with unprecedented depth and continuity. The distinction Taylor drew between a basic chatbot and an agentic AI is profound. While chatbots often operate on rigid, rules-based logic, an AI agent, deriving its name from the concept of “agency,” is empowered to be creative and make autonomous decisions within defined goals and guardrails. This allows for a level of empathy and problem-solving previously thought exclusive to human interaction. Taylor cited the example of a canceled flight, a frustrating experience often exacerbated by impersonal, script-driven customer service. An agentic AI, he suggested, could leverage its perfect access to information, multilingual capabilities, and instant availability to offer “unreasonable hospitality,” such as a free coffee or loyalty points, anticipating needs and proactively mitigating distress. Indeed, the economic benefits of this shift are staggering. A typical human-led customer service call today costs a company approximately $25. This high cost limits personalized interaction, especially for businesses with millions of customers or those offering lower-priced products where the average revenue per user (ARPU) is less than the cost of a single support call. Agentic AI democratizes personalized engagement, making it economically viable to have tailored conversations with every customer, regardless of scale. This isn’t just about cost reduction; it’s about transforming customer relationships from reactive problem-solving to proactive, empathetic brand ambassadorship. Taylor highlighted how Sierra’s AI agents are already demonstrating superior performance. The Weight Watchers agent, powered by Sierra, has achieved “higher empathy scores than the coaches in their call center.” This underscores the potential for AI to not just replicate human capabilities but to exceed them in specific, measurable ways, particularly in scenarios demanding patience, consistent information recall, and rapid processing of complex data. However, this ambitious vision is not without its challenges, particularly concerning the underlying infrastructure. The immense computational power required to train and run these sophisticated AI models is becoming the “limiting factor” for the growth of leading AI companies like OpenAI. Taylor explained that large data centers are crucial for two phases of the AI pipeline: training the models and inference (the process of running the trained models to make predictions or generate responses). For modern models, inference is particularly demanding, requiring substantial GPU resources to facilitate complex “chain of thought reasoning” – essentially, the AI thinking aloud to arrive at a solution. Related Reading The rapid pace of technological obsolescence in the compute space adds another layer of complexity. Unlike traditional infrastructure investments, such as laying down train tracks or fiber optic cables, the lifespan of AI-specific hardware, like NVIDIA chips, is relatively short. Investors face the reality that these expensive components may need replacement every few years to keep pace with innovation, posing a significant capital expenditure challenge. This creates a unique economic dynamic, where the upfront investment is massive, and the depreciation cycle is accelerated. Despite these hurdles, Taylor remains optimistic. He believes the market will adapt, and the focus will shift towards building the largest possible compute infrastructure to meet the burgeoning demand for AI. He also emphasized that the future isn’t about a single, monolithic AI model. Instead, engineers and applied AI companies will strategically mix and match various models across a spectrum of cost, quality, latency, and speed to suit specific tasks. A low-latency phone conversation, for instance, might demand a fast, relatively inexpensive model, while complex actuarial sciences would prioritize accuracy, regardless of computational cost. This nuanced approach to model deployment will be critical in optimizing both performance and economics as AI continues to permeate every sector of the economy. Don't miss a beat
Sierra Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When was Sierra founded?
Sierra was founded in 2023.
Where is Sierra's headquarters?
Sierra's headquarters is located at 150 Sutter Street, San Francisco.
What is Sierra's latest funding round?
Sierra's latest funding round is Series D.
How much did Sierra raise?
Sierra raised a total of $635M.
Who are the investors of Sierra?
Investors of Sierra include Greenoaks, ICONIQ Capital, Thrive Capital, Sequoia Capital, Benchmark and 9 more.
Who are Sierra's competitors?
Competitors of Sierra include Giga, Aisera, Scaled Cognition, Ema, AgentifAI and 7 more.
Loading...
Compare Sierra to Competitors

Decagon operates as a company that focuses on conversational Artificial Intelligence (AI) within the technology sector. The company provides a platform for creating and optimizing Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents to offer customer support across channels like chat, email, and voice. The company serves various sectors, including retail, travel, technology, financial services, health, media, and telecommunications. It was founded in 2023 and is based in San Francisco, California.

Ada specializes in artificial intelligence (AI) powered customer service automation within various business sectors. The company offers a platform that enables enterprises to resolve customer inquiries efficiently across multiple channels and languages without the need for extensive human intervention. Ada's solutions cater to industries such as e-commerce, financial technology, software as a service (SaaS), and gaming. It was founded in 2016 and is based in Toronto, Canada.

Leena AI provides enterprise artificial intelligence (AI) solutions within the technology sector. The company offers automation for information technology (IT), human resources (HR), and finance processes, leveraging Agentic AI to reduce service tickets and facilitate self-service for employees. Leena AI's products aim to integrate with various enterprise applications. It was founded in 2015 and is based in San Francisco, California.

Inbenta specializes in conversational AI and automation within the customer service sector. The company offers a suite of products, including AI-enabled chatbots, search tools, and knowledge management systems designed to enhance customer experience and streamline service operations. Inbenta's conversational AI platform is utilized across various industries to automate customer interactions, provide self-service options, and improve overall customer satisfaction. It was founded in 2005 and is based in Allen, Texas.

Intercom operates as an artificial intelligence (AI) customer service company that operates within the customer support industry. The company provides AI tools that aim to improve customer service efficiency. Intercom serves businesses that are interested in utilizing AI technology for their support operations. It was founded in 2011 and is based in San Francisco, California.
![[24]7.ai Logo](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/cbi-image-service-prd/original/b029c933-1e02-401f-bb6b-777a5d7ed5b5.png)
[24]7.ai provides artificial intelligence (AI)-based customer service products and solutions. It offers solutions such as conversation automation solutions, workforce engagement solutions, campaign management solutions, and more. [24]7.ai was formerly known as 24/7 Customer. It was founded in 2000 and is based in Campbell, California.
Loading...
