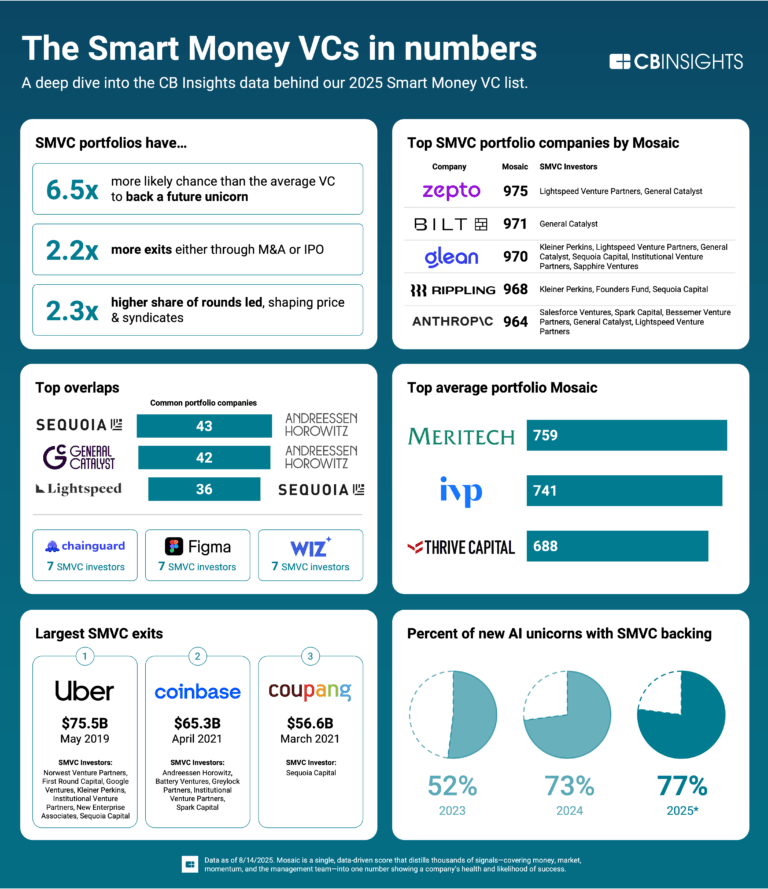
Torq
Founded Year
2020Stage
Series C | AliveTotal Raised
$190MLast Raised
$70M | 1 yr agoRevenue
$0000Mosaic Score The Mosaic Score is an algorithm that measures the overall financial health and market potential of private companies.
+30 points in the past 30 days
About Torq
Torq specializes in security hyper-automation within the cybersecurity industry. It offers a no-code platform that unifies and automates security workflows and infrastructure, helping in productivity and protection for enterprise security teams. Torq was formerly known as StackPulse. The company was founded in 2020 and is based in Tel Aviv, Israel.
Loading...
Torq's Product Videos

ESPs containing Torq
The ESP matrix leverages data and analyst insight to identify and rank leading companies in a given technology landscape.
The security operations center (SOC) AI agents & copilots market provides AI-powered solutions that enhance cybersecurity analysts' response and threat detection capabilities within security operations centers. These solutions range from autonomous AI agents that independently investigate alerts and take bounded actions to AI copilots that assist analysts through guided workflows and recommendatio…
Torq named as Leader among 15 other companies, including Blink, Tines, and ReliaQuest.
Torq's Products & Differentiators
Torq
No-code automation for cybersecurity teams.
Loading...
Research containing Torq
Get data-driven expert analysis from the CB Insights Intelligence Unit.
CB Insights Intelligence Analysts have mentioned Torq in 3 CB Insights research briefs, most recently on Sep 3, 2025.
Mar 6, 2025
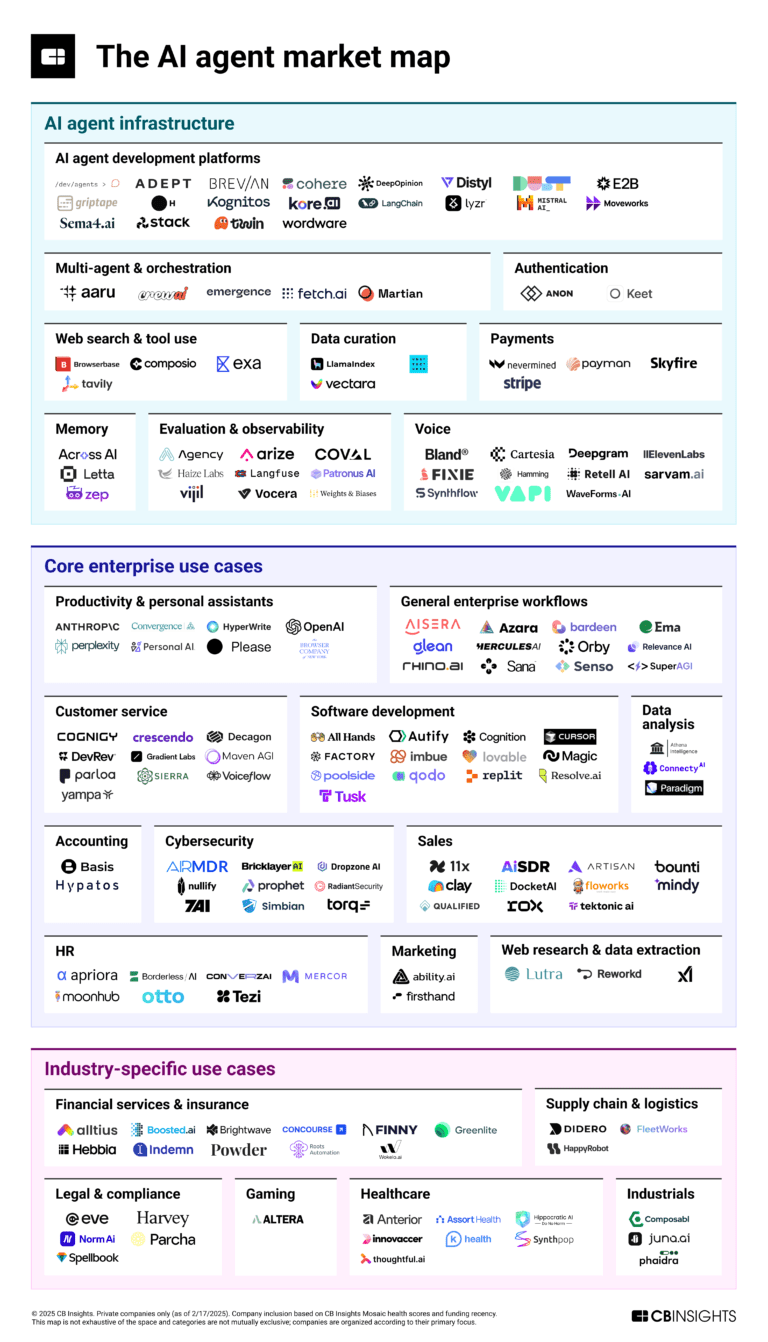
The AI agent market map: March 2025 edition
Aug 7, 2024
The enterprise AI agents & copilots market mapExpert Collections containing Torq
Expert Collections are analyst-curated lists that highlight the companies you need to know in the most important technology spaces.
Torq is included in 6 Expert Collections, including Cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity
11,028 items
These companies protect organizations from digital threats.
AI Agents & Copilots Market Map (August 2024)
322 items
Corresponds to the Enterprise AI Agents & Copilots Market Map: https://app.cbinsights.com/research/enterprise-ai-agents-copilots-market-map/
AI agents (March 2025)
376 items
Companies developing AI agent applications and agent-specific infrastructure. Includes pure-play emerging agent startups as well as companies building agent offerings with varying levels of autonomy. Not exhaustive.
Generative AI
2,951 items
Companies working on generative AI applications and infrastructure.
AI agents & copilots
1,777 items
Companies developing AI agents, assistants/copilots, and agentic infrastructure. Includes pure-play emerging agent startups as well as companies building agent offerings with varying levels of autonomy.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
9,236 items
Torq Patents
Torq has filed 1 patent.
The 3 most popular patent topics include:
- drilling technology
- fluid dynamics
- piping

Application Date | Grant Date | Title | Related Topics | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
4/3/2023 | 10/1/2024 | Wrenches, Fluid dynamics, Plumbing, Piping, Drilling technology | Grant |
Application Date | 4/3/2023 |
|---|---|
Grant Date | 10/1/2024 |
Title | |
Related Topics | Wrenches, Fluid dynamics, Plumbing, Piping, Drilling technology |
Status | Grant |
Latest Torq News
Oct 27, 2025
Security Boulevard Community Chats Webinars Library Innovative Strategies for NHI Security How Secure Are Your Non-Human Identities in the Cloud? Where technology continuously evolves, how confident are you in your Non-Human Identities (NHIs) within cloud environments? These NHIs, essentially machine identities, serve as critical components in modern cybersecurity frameworks. Their management is pivotal for securing sensitive assets and ensuring operational integrity across various sectors. From financial services and healthcare to travel, DevOps, and SOC teams, the demand for robust NHI management transcends multiple industries, particularly those leveraging cloud technologies. Understanding Non-Human Identities in Cybersecurity Non-Human Identities refer to machine identities used. These identities are created by combining a “Secret” (like an encrypted password, token, or key) and the permissions accorded to that Secret by a destination server. Much like how a passport identifies a person, NHIs help establish the identity of systems and machines within a network. The permissions are akin to a visa, granting certain access privileges based on this identity. Properly managing these aspects—identities (the “tourist”) and their access credentials (the “passport”)—ensures smoother, safer operations. The crux of effective NHI security lies in understanding the complete lifecycle of these identities—from discovery and classification to threat detection and mitigation. This comprehensive approach offers more robust protection than point solutions, such as secret scanners, which only offer limited scope. By employing a holistic management strategy, organizations can provide contextual insights into ownership, permissions, usage patterns, and vulnerabilities. Benefits of Effective NHI Management Adopting a comprehensive strategy for NHI management yields several advantages: Reduced Risk: Proactively identifying and addressing potential security threats helps lower the risk of breaches and data leaks. Improved Compliance: Effective management supports organizations in meeting regulatory requirements through policy enforcement and detailed audit trails. Increased Efficiency: Automation of NHIs and secrets management allows security teams to devote attention to strategic initiatives instead of routine tasks. Enhanced Visibility and Control: A centralized view facilitates better access management and governance. Cost Savings: Automation of secrets rotation and NHIs decommissioning can lead to significant reductions in operational costs. Innovative Strategies for NHI Security Organizations looking to enhance their NHI management can adopt several innovative strategies to ensure machine identities remain secure. 1. Advanced Integration Platforms: Adopting platforms that integrate seamlessly with existing security infrastructures can enhance the oversight and management of NHIs. For example, platforms that facilitate integrations with leading security tools can provide a more cohesive management framework. Consider exploring the Entro-Wiz Integration for more insights. 2. Behavioral Monitoring: Implementing systems that monitor the behavior of NHIs can provide early detection of anomalies, allowing for quick intervention and threat neutralization. This strategic approach significantly enhances the security posture of any organization operating in the cloud. 3. Dynamic Secrets Management: Utilizing dynamic secrets, which change frequently and automatically, then making them an integral part of the NHI management strategy. This reduces risks associated with static credentials, which can be vulnerable if exposed. 4. Lifecycle Management: Addressing all lifecycle stages of NHIs ensures comprehensive security oversight. From deployment to decommissioning, ensuring each phase is robustly managed is crucial. More detailed insights can be accessed through Non-Human Identities Security in Healthcare . 5. Enhanced Collaboration Between Teams: Bridging the gap between security and R&D teams fosters a more secure cloud. Encouraging communication and shared objectives helps mitigate potential security gaps that could be exploited. 6. Real-time Threat Detection: Employing real-time analytics can help, allowing organizations to react swiftly and effectively. This proactive stance is pivotal where threats are increasingly sophisticated. The Strategic Importance of NHI Security Non-Human Identity security is not merely a technical requirement but a strategic priority that impacts business continuity and safety. By focusing on securing machine identities and their associated secrets, organizations can ensure safer, more reliable operations, fostering trust among stakeholders and compliance with regulations. Given the complexity and potential vulnerabilities, the strategic management of NHIs becomes a non-negotiable aspect of modern cybersecurity strategies. For organizations committed to comprehensive security control, integrating NHI and secrets management into their cybersecurity strategies is essential. For further insights into this strategic integration, take a look at this Agentic AI OWASP Research . The ongoing evolution within cloud-based solutions makes it imperative for organizations to remain vigilant and proactive in their security strategies. By leveraging innovative methodologies and ensuring dynamic NHI management, organizations can significantly mitigate risks, achieve compliance, improve efficiency, and maintain robust visibility and control over their digital ecosystems. Each decision to enhance NHI security is a step towards a more resilient and fortified cyber defense framework, ensuring both present security and future readiness. The Emerging Challenges in NHI Management How do expanding technological environments and evolving threats impact the management of Non-Human Identities effectively? Where organizations increasingly rely on cloud infrastructures, the management of machine identities—NHIs—becomes increasingly complex. The dual challenge emerges: ensuring that NHIs have the required access while shielding these points of access from malicious actors. Several factors contribute to the growing complexities: 1. Diverse Cloud Environments: With organizations utilizing hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, NHIs are expected to operate across varied platforms, each with unique constraints and requirements. Ensuring seamless operation across these environments poses considerable security and operational challenges. 2. Increased Automation: With organizations automate more processes, the number of NHIs increases exponentially. Every robot process, application, or system integration function needs an identity, meaning that managing these at scale effectively without introducing vulnerabilities becomes a critical task. 3. Regulatory Compliance Pressure: Organizations must navigate a complex web of local and international privacy and security regulations. Effective NHI management helps businesses not only achieve compliance but also maintain it over time. The dynamic nature of regulatories demands continuous adaptation and vigilance. 4. Sophistication of Threats: Cyber adversaries are increasingly targeting NHIs due to their often weaker security postures. When machine identities are exploited, organizations must employ advanced threat detection and mitigation strategies to stay ahead. Navigating NHI Security with Best Practices Implementing best practices is essential for robust NHI security: Comprehensive Inventory Management: Maintain an up-to-date inventory of all machine identities within your organization. This aids in understanding and managing the scope of your security efforts. Access Control Policies: Employ least privilege access principles. NHIs should receive only the permissions necessary for their functions. Regular audits ensure these permissions stay aligned with business needs. Automated Secret Management: Leverage automated tools to handle secret rotations and ensure secrets do not become outdated or vulnerable. Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular assessments to identify vulnerabilities in NHI management and address them promptly. Internal and external audits can provide insights into potential security gaps. Incident Response Planning: Establish clear action plans for potential breaches involving NHIs. A structured response can significantly mitigate damage and facilitate faster recovery. Dive into Best Practices for Building an Incident Response Plan for detailed strategies. These practices combine to create a solid foundation for NHI security, providing a buffer against threats while aligning with strategic objectives. Future Directions in NHI Management What advancements can organizations anticipate as they enhance their NHI management strategies? Continuous technological evolution creates opportunities to refine and advance the management of Non-Human Identities: 1. AI and Machine Learning: These technologies will offer predictive insights and advanced threat detection capabilities. By analyzing behavior patterns, these solutions will identify anomalies that suggest potential security risks, allowing for proactive measures. 2. Blockchain for Identity Verification: Blockchain technology holds promise for enhancing the security of machine identities through tamper-proof verification and transparency. 3. Unified Security Frameworks: Comprehensive frameworks that integrate NHI management with broader cybersecurity policies can reduce silos and improve coherence across security practices. 4. Edge Security Solutions: When edge computing becomes more prevalent, solutions ensuring the security of NHIs operating at the network’s edge will become paramount. 5. Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Security is not solely the domain of IT departments. Collaboration between Security, DevOps, R&D, and other departments fosters interdisciplinary threat intelligence and response strategies. The Collaborative Approach to NHI Security Ensuring robust Non-Human Identity security requires a collaborative approach across the organization. Bridging the traditional silos between security and R&D is pivotal in nurturing a seamless and vigilant security environment. Collaborative frameworks encourage: – Unified Objectives: Establishing common security goals across departments ensures cohesive security practices and aligns organizational priorities. – Shared Insights and Intelligence: Departments that share threat intelligence can respond to security incidents more swiftly and effectively. This knowledge transfer enhances the overall robustness of security frameworks. – Cross-Training Programs: Implementing training programs where teams exchange knowledge on different aspects of cybersecurity enriches the organizational capability to handle NHIs effectively. Allowing different departments to contribute their unique perspectives on NHI management enhances the resilience and efficiency of security strategies. For organizations seeking to foster stronger collaborations in this domain, a partnership approach is instrumental, as highlighted in Entro’s collaboration with Torq . Unfolding NHI management demands not only awareness and vigilance but innovative solutions and strategic collaborations, ensuring security measures remain as dynamic and adaptable as the environments they protect. *** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Entro authored by Alison Mack . Read the original post at: https://entro.security/innovative-strategies-for-nhi-security/
Torq Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When was Torq founded?
Torq was founded in 2020.
Where is Torq's headquarters?
Torq's headquarters is located at HaMelacha 3, Tel Aviv.
What is Torq's latest funding round?
Torq's latest funding round is Series C.
How much did Torq raise?
Torq raised a total of $190M.
Who are the investors of Torq?
Investors of Torq include Bessemer Venture Partners, Notable Capital, Greenfield Partners, Evolution Equity Partners, Strait Capital Investment Group and 6 more.
Who are Torq's competitors?
Competitors of Torq include Bricklayer AI, Prophet, Dropzone AI, Blink, Swimlane and 7 more.
What products does Torq offer?
Torq's products include Torq.
Who are Torq's customers?
Customers of Torq include Lemonade and Agoda.
Loading...
Compare Torq to Competitors

Intezer focuses on the development of its Autonomous SOC Platform designed to support security operations. The company offers solutions for the triage, investigation, and remediation of security alerts, with the aim of automating incident response processes. Intezer's technology is primarily utilized by security operations centers (SOCs) to assist analysts by resolving false positives and escalating serious threats. It was founded in 2015 and is based in New York, New York.

Tines is a workflow automation platform that focuses on security and information technology (IT) solutions across various business sectors. The company provides a platform that allows teams to automate tasks and integrate with technologies through application program interfaces (APIs). Tines serves sectors including security, IT, infrastructure, engineering, and product development. It was founded in 2018 and is based in Dublin, Ireland.

Dropzone AI specializes in security operations automation within the cybersecurity industry. The company offers pre-trained autonomous AI security agents that conduct thorough, end-to-end investigations of security alerts, mimicking the techniques of analysts. Dropzone AI's solutions are designed to integrate with existing security tools, providing detailed reports and enabling security analysts to focus on threats. It was founded in 2023 and is based in Seattle, Washington.

Prophet focuses on automating security operations through its platform. It provides solutions that triage, investigate, and respond to security alerts, which may reduce investigation time and improve operational efficiency. It serves sectors that require cybersecurity measures, such as technology, finance, and healthcare. It was founded in 2024 and is based in Atherton, California.

Radiant Security provides security and monitoring services. The company offers an artificial intelligence (AI) security operations center (SOC) co-pilot that automates the triage and investigation of security incidents, helps to enhance analyst productivity, and detects real attacks, and response times. It services the cybersecurity sector. The company was formerly known as BlastRadius. It was founded in 2021 and is based in Milpitas, California.

AirMDR specializes in the domain of Security Operations. The company's main offering is a virtual assistant designed to assist in Security Operations, providing services such as task management, question answering, and continuous learning and adaptation. The primary sector AirMDR caters to is the cybersecurity industry. The company was founded in 2023 and is based in Menlo Park, California.
Loading...